Q77. What is RPD?
Ans. RPD is defined as any prosthesis that replaces some teeth in a partially dentate arch.It can be removed from the mouth and replaced at will-also called partial removable dental prosthesis.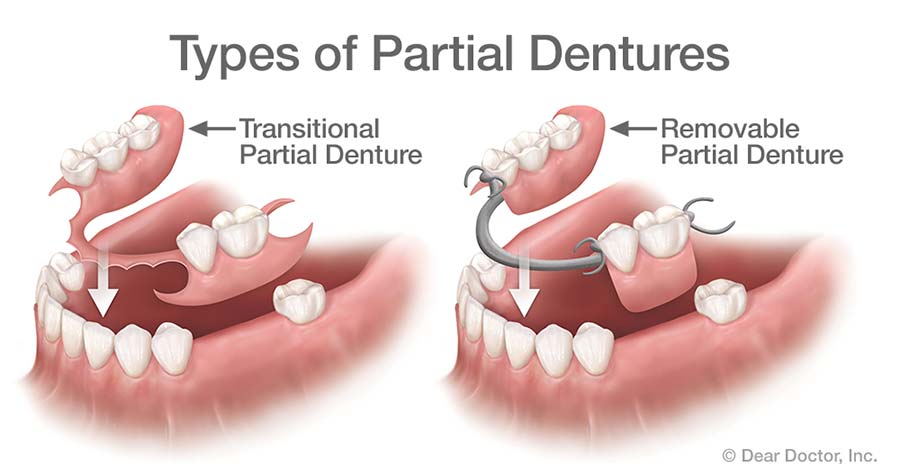
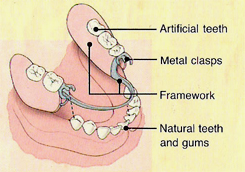
Q78. What are the components of RPD?
Ans. The components of removable partial denture are:
Q79. What is a major connector?
Ans. The part of a partial removable dental prosthesis that joins the components on one side of the arch to the components on opposite side.

Enter your email address to receive our Free Newsletter for key Exam and Resource Updates