BASAL CELL CARCINOMA 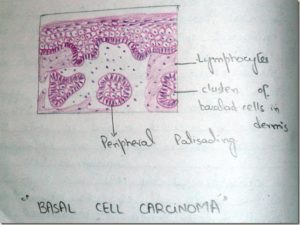
OTHER NAME – Rodent ulcer
CLINICAL FEATURES–
- Basal cell carcinoma is a disease of adult whites
- Most prevalent in patients older than 40 years
- Malesare most commonly affected
- Incidenceof BCC is high in areas with high temperature and low humidity
- Site – commonly occurs cover the hair bearing areas of facial skin (especially mucocutaneous areas)
- Orofacial areas are particularly vulnerable to lesion are upper lip, nasolabial folds, periorbital region,cheek, forehead,ear etc.
- The most common form of this lesion , the nodular ( noduloulcerative) BCC , begins as a firm, painless papule that slowly enlarges and gradually develops a central depression and an umbilicated appearance
- The lesion invades the mucous membrane by directly spreading from the adjacent skin
- It is slow growing, slightly elevated small nodule
- Eventually develop into central,crusted ulcer with an elevated, smooth- rolled border
- Lesion heal partially by scarring in central area but it keeps on spreading centrifugally
- When the lesion is pressed, a characteristic pearly opalescent quality is discerned Expanding ulceration often develops in the central depressed area and and patient gives history of bleeding followed by healing
- “Rodent ulcer ” name is given to this tumor as it makes a slow but relentless progress and increases in size by invading and destroying adjoining tissues.
HISTOPATHOLOGY:
- Characterised by neoplastic proliferation of basaltic epithelial cells in the form of multiple solid islands
- Cells in periphery of tumor islands are columnar in shape and they often resemble basal layer of oral epithelium with hypercholesterolemia nuclei
- Tumor cells do not show any feature of abnormal mitosis
- Central cells of tumor islands may be polyhedral, oval, round or even spindle shaped
- Basal cell carcinoma sometimes resembles ‘Follicular Ameloblastoma’.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
- Ameloblastoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
TREATMENT
- Surgical excision of electrocuted you alongwith radiotherapy
- Prognosis extremely good
- Cure rate 95%

